Engineering Workshop"

The engineering workshop provides basic knowledge on various hand tools and their usage required for manufacturing processes. The tools include Carpentry, Fitting, House wiring, Black smithy, Tin smithy. The practical knowledge gained at workshop helps students in understanding the activities and practical difficulties of skilled workman involved in producing goods when they occupy executive positions in the industries. In this lab students learn about usage of engineering tools and equipment and also to perform experiments on basic production methods
The facilities available in the laboratory
Fitting : |
Tin Smithy: |
Carpentry: |
||
| a) Work Benches | a) Work tables | a) Work Tables | ||
| b) Bench vice | b) Snips | b) Wood Turning Lathe | ||
| c) Drilling Machine | c) Stakes | c) Hand Saw, Tenon Saw | ||
| d) Power Hacksaw machine | d) Mallets | d)Chisels | ||
| e) Grinding machine | ||||
| f) Chop saw | ||||
House Wiring: |
Black smithy: |
Foundry: |
||
| a) Cubicals | a) Anvils | a) Moulding Boxes | ||
| b) Pipe Cutter, Wire Cutter, Wire remover etc | b) Open Furnace | b) Furnace | ||
| c) Electrical Air Blower | c) Patterns | |||
| d) Mechanical Air Blower | d) Risers, Runners, Gate cutter, Showel, Trowel etc. | |||
| e) Swage Block |
Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery


Fluid mechanics, a branch of continuum mechanics, is of paramount interest to mechanical engineers as they come across fluids in many mechanical systems such as turbines (steam, hydraulic, gas), compressors, pumps, aero-systems, IC engines, refrigeration, HVAC systems, etc. For proper and optimum design of above systems it is important for mechanical engineers to have a thorough understanding of the principles of fluid mechanics. The principles of conservation of mass, momentum and energy form the basis of the study of fluid mechanics. In this laboratory the students have the opportunity to perform various experiments to understand the above theoretical principles. The students will perform tests on buoyancy; test the Bernoulli’s theorem and its applications in flow measurement devices; study the different types of fluid flows; understand the forces acting on various types of vanes used in hydraulic machinery. The laboratory also caters to the student’s understanding of the working principles of hydraulic machinery. They get the opportunity to study the performance characteristics of hydraulic machinery such as Pelton wheel, Kaplan and Francis turbine and Centrifugal pumps, Gear and Vane pumps, Jet pump and Submergible pumps. The measurement of flow in water channels, irrigation canals, the study of dimensional and model analysis of structures such as dams and weirs is of importance to Civil engineers. The laboratory is equipped with multipurpose tilting flume flow set up for the above purpose. The facilities available in the laboratory |
|
| 1) Buoyancy testing setup. 2) Reynolds apparatus. 3) Bernoulli’s theorem setup. 4) Computerized pipe flow loss analysis set up. 5) Computerized set up for calibration of Venturimeter and Orificemeter. 6) Computerized set up for calibration of flow over notches and weirs. 7) Turbine flow meter. 8) Impact of jet on vanes. 9) Pelton Wheel. 10) Kaplan Turbine. 11) Francis Turbine. 12) Single and Multistage Centrifugal Pumps. 13) Jet pump. 14) Submergible pump. 15) Gear and Vane pump. 16) Multipurpose tilting flume set up. |
Production Technology


Production technology involves transformation of raw materials in to products using various manufacturing process. Mechanical engineers have to gain knowledge about various conventional and modern manufacturing processes for producing human needed products. This lab transforms theoretical knowledge into practical knowledge. In this lab, students perform experiments on various manufacturing processes like Casting, Forging, Welding, Plastic moulding etc and learn how to make products. The facilities available in the laboratory |
|
1) Arc Welding Machine (400 Amps) |
Mechanics of Solids

A Mechanical Engineer often comes across the task of performing analysis of materials used in structural applications. A “structure” may be defined as any design that uses materials to support loads and keeps deformation within acceptable limits. The task of the design of structures and machines, which are reliable and safe, requires a proper knowledge of engineering as well as material selection. Mechanics of solids or strength of materials is the study of deformation and behavior of a body due to mechanical, thermal, or other loads. The basis of all mechanical design lies in how the material reacts to outside forces. Hence, an in-depth understanding of material properties as well as how materials react to outside stimulus is important to a mechanical engineer. In this laboratory, students will have the opportunity to perform various experiments. The student will perform tests on materials in tension, torsion, bending, and buckling. These conditions and/or constraints are designed to reinforce classroom theory by having the student perform required tests, analyze subsequent data, and present the results in a professionally prepared report. The facilities available in the laboratory |
|
| 1) Computerized Universal Testing Machine. 2) Torsion test machine. 3) Spring testing machine. 4) Hardness testing machine (Rockwells and Brinells) 5) Fatigue testing machine. 6) Izod and Charpy test machine. |
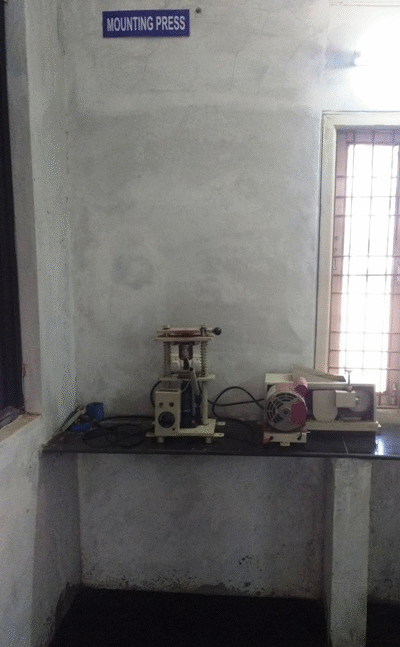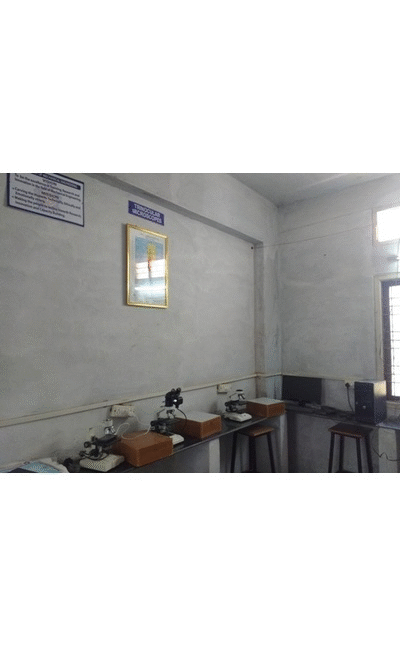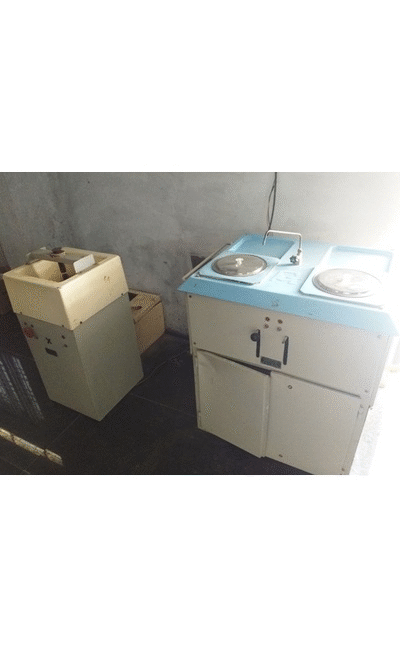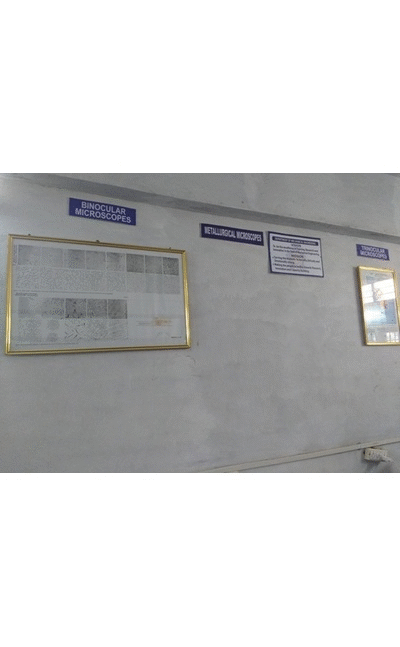
Metallurgy and Material Science
Thermal Engineering


Thermal engineering deals with the conversion of energy to useful work, mainly the conversion of heat energy to work. Thermal engineering needs a good understanding of the principles of Thermodynamics, Heat transfer and Fluid mechanics. Thermal engineering finds applications in many fields such as working of IC engines, HVAC, Refrigeration, Power plant systems etc. Thermal engineering laboratory helps students to understand the basic principles of energy conversion mainly in IC engines. Internal combustion engines have revolutionized the transportation sector and greatly contributed to the human endeavor. Current efforts to increase the efficiency of engines and greater emphasis to meet the environmental regulatory norms have increased the research efforts in this field. Hence, it is imperative that students have a good understanding of the principles of working of IC engines. In this laboratory, students will have the opportunity to perform experiments to understand the principles such as valve and port timing diagrams and their importance; understand difference between two and four stroke engines; understand the performance parameters of SI and CI engines; to obtain heat (energy) balance in an engine and understand the energy conversion mechanism etc. These experiments help students to reinforce the theoretical principles taught in the classroom and give them a good foundation to understand the energy conversion process. The facilities available in the laboratory |
|
| 1) Cut view of 2 stroke engine for Port time diagram. 2) Cut view of 4 stroke engine for Valve time diagram. 3) 2 Stroke SI engine set up. 4) 4 Stroke CI engine set up. 5) 4 Stroke SI engine set up. 6) Reciprocating Air compressor. |
Metrology and Surface Engineering

Metrology is a part of the production process. At the end of finishing operation, the products have to be checked to conform to the measurements, accuracy and tolerances. This laboratory deals with the measurement of linear, angular and surface roughness measurements. Various types of instruments are being used and their accuracy ascertained with the help of standards like slip blocks and sine bar. In this laboratory students learn about various instruments and inspection methods which are used in the industries. The facilities available in the laboratory |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Machine Tools

This laboratory is aimed at providing an introduction to the Know-how of common processes used in industries for manufacturing parts by removal of material in a controlled manner. Auxiliary methods for machining to desired accuracy and quality will also be covered. The emphasis throughout the laboratory course will be on understanding the basic features of the processes rather than details of constructions of machine, or common practices in manufacturing or acquiring skill in the operation of machines. Evidently, acquaintance with the machine is desirable and the laboratory sessions will provide adequate opportunity for this. The facilities available in the laboratory |
|
| 1) High Speed Precision Lathe-NH22/100 (HMT) 2) Conventional Lathes (Pinachoo) 3) Radial Drilling Machine-RM62 (HMT) 4) Milling Machine-FN2U(HMT) 5) Hydraulic Cylindrical Grinding Machine-ANUBAVK130/500 (HMT) 6) Universal Cutter &Tool Grinding Machine (HMT) 7) Precision Surface Grinding Machine (HMT) 8) Shaping Machine |
Heat Transfer


Heat transfer is the passage of thermal energy from a hot to a cold body. When a body, an object or fluid, is at a different temperature than its surroundings, transfer of thermal energy takes place in such a way that the body and the surroundings reach thermal equilibrium and this type of transfer of energy is known as Heat transfer. Heat transfer always occurs from a hot body to a cold body, a result of the second law of thermodynamics. Heat transfer occurs through conduction, convection, radiation or any combination of these. Almost all mechanical processes result either in the production or in the absorption of heat and therefore are affected by heat. Understanding the mechanisms of heat transfer is of particular interest to engineers, who attempt to understand and control the flow of heat in mechanical systems design. In this laboratory, students will have the opportunity to perform experiments to understand the three modes of heat transfer, namely, conduction, convection and radiation. Experiments on heat conduction through a metal rod, composite slabs and concentric spheres, applications such as pin-fins, heat pipes, heat exchanger, natural and forced convection, and Stefan-Boltzmann’s experiment reinforce the theory taught in the classroom and gives them a good foundation for understanding the physics of heat transfer problems. The facilities available in the laboratory |
|
| 1) Concentric spheres setup. 2) Thermal conductivity of metal rod setup. 3) Pin-fin apparatus. 4) Heat pipes setup. 5) Lagged pipe setup. 6) Composite slabs setup. 7) Transient heat conduction setup. 8) Natural convection apparatus. 9) Forced convection apparatus. 10) Critical heat flux apparatus. 11) Film and Drop wise condensation unit 12) Parallel and counter flow heat exchanger. 13) Emissivity apparatus. 14) Stefan-Boltzmann apparatus. |
CAD-CAM

CAD-CAM lab provides a space where real application of computer to Mechanical Engineering can be realized. CAD introduces computer to design a component and CAM explains how computer can be best utilized to automate manufacturing system. In the lab, students explore and learn to use software for designing a component. This lab provides a good hand on experience for the students to compete challenges of recent trends as Mechanical Engineer.
The facilities available in the laboratory
1) AutoCAD.
2) Pro/ENGINEER.
3) ANSYS
4) FlexSim.
5) NX CAD / CAM / CAE.
Instrumentation and Control system

Instrumentation is one of the parts of the quality control process. To manufacture a part to the exact dimension and to test the quality of the products, the instruments should be calibrated against a known higher standard. It is therefore essential to calibrate the instruments regularly for high accuracy and repeatability of the measurements. In this lab, the students learn about calibration of various instruments namely thermocouples, transducers etc. The facilities available in the laboratory |
|
| 1) Resistance Temperature Detector 2) Transducer 3) Thermocouple 4) LVDT Transducer 5) Magnetic Speed Pickup 6) Level Indicator 7) Mcloid gauge 8) Rotameter 9) Sesimic pickup setup 10) Dead weight pressure gauge 11) Strain gauge |